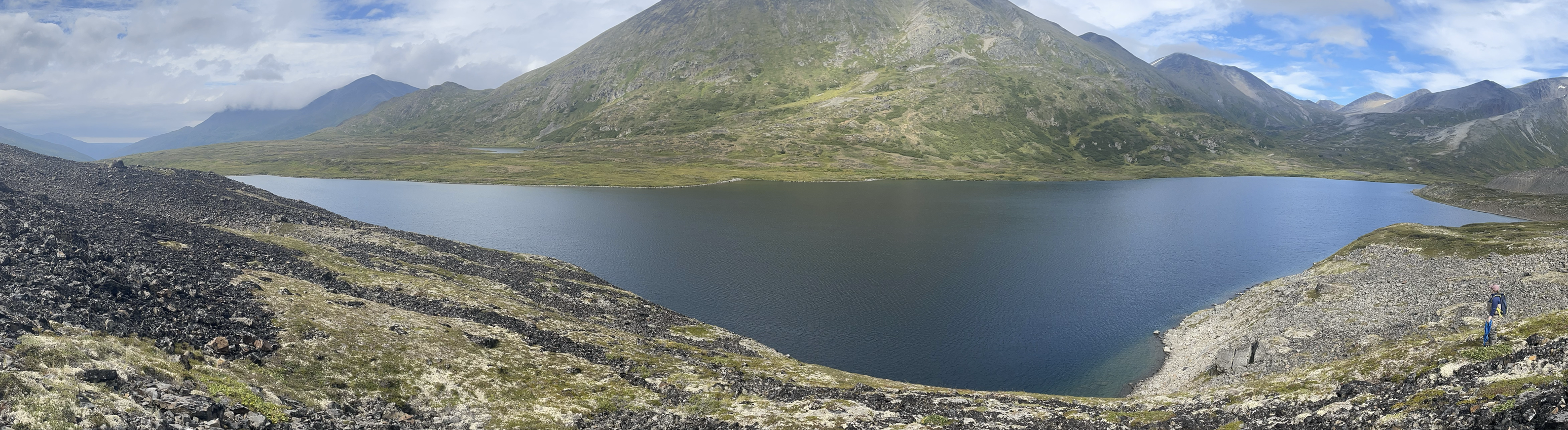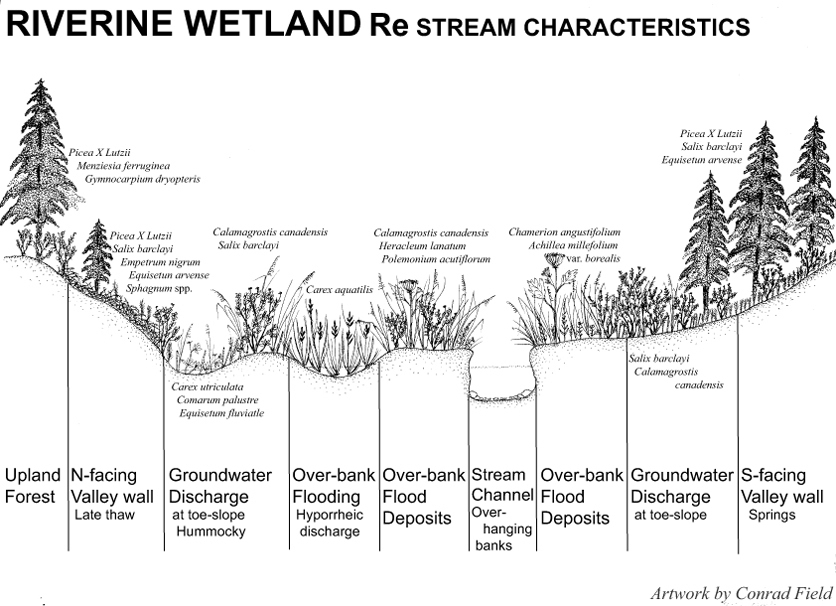
An idealized cross-section of an Re stream valley showing key characteristics and typical plants of local underfit streams. Drawing by Conrad Field.
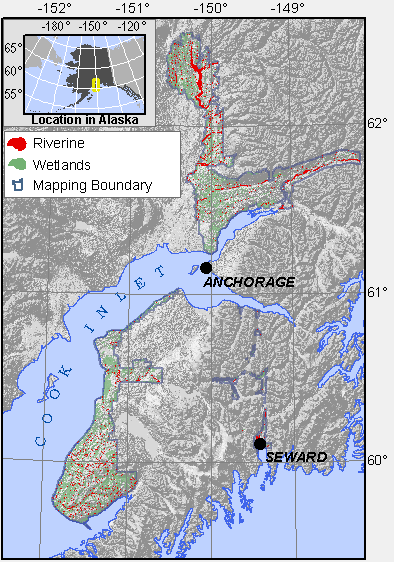
Range of wetlands mapped as Riverine.
Riverine wetlands lie adjacent to rivers and streams. The Cook Inlet Classification uses a modified version of Rosgen & Silvey’s classification (1996) to name these wetlands. Level I of Rosgen’s system has seven classes, four of which are common on the lowlands: Types B, C, D, and E (Fig. 1):
B reaches are moderately entrenched, riffle-dominated reaches with narrow fringing wetlands;
C reaches possess riffle/pool morphology with point bars and broad fringing wetlands on floodplains;
E reaches are slightly entrenched, stable, pool- dominated channels within relict channels (underfit) supporting wide stream fringe wetlands; and
D reaches are braided glacial rivers.
A fifth type, DA, is used to describe a small, multiple channel stream reach and associated wetlands as the reach fans out onto a glacial terrace, usually in a peatland.
Steep, entrenched A stream reaches, with rapids, waterfalls, and narrow associated wetland margins, occur along a few streams flowing into Kachemak Bay, such as McNeil and Falls Creek.
 An aerial image of a B reach draining the Epperson Knob area on the southern Kenai Lowlands. Notice the deeply entrenched channel, with very narrow fringing wetlands |
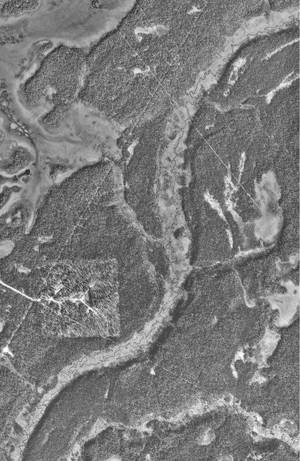 An aerial image of an E reach, along the the middle portion of the Ninilchik River. Notice the mismatch between the meander geometry of the valley and the modern stream channel. |
 An aerial photo of an RDA reach flowing from a channel in the forest at the right of the photo, to a braided stream across the peatland, and again becoming channelized at left. |
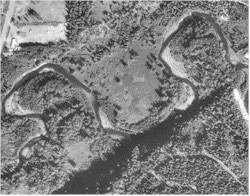 An aerial photo of a C reach, Deep Creek, east of the Sterling Highway. Notice the cut-banks at outer bends and point bars at inside bends |
 An aerial photo of a D reach, the Resurrection River west of the Seward Highway. Notice the multi-threaded channel and the numerous short, clearwater channels originating from hyporrheic flow (the short, dark-colored branches flowing into the silty main threads). |
Many streams originate as moderately entrenched B reaches. The dominant B types at level II in Rosgen’s classification are B4, with moderately steep valley walls and beds dominated by gravels, and B3 where cobbles dominate the bed material. B reaches have very narrow wetland fringes, if at all.

A wide B reach, the East Fork, along the Seward Highway. Fringing wetlands are absent, or very narrow.
Type B reaches frequently flow into Type E reaches (E for “evolutionary”). E reaches are slightly entrenched, stable, low-gradient, pool-dominated reaches with low width/depth ratios, densely vegetated banks, and low sinuosity (although the typical Rosgen E reach has high sinuosity). E reaches have narrow active floodplains even though steep valley walls may be distant from the modern channel. Occasionally, abandoned channels and oxbows are evident.
E reaches occur on relict glacial lakebeds or within wide valley bottoms that were eroded by large amounts of glacial meltwater at the last glacial maximum. A good example of an E reach is the upper portion of the Ninilchik River, which flows along a glacial terrace. The unnamed creek between Palmer and Wasilla that orginates near Memory Lake and disappears into gravel near Vine road is another good example of an E reach. The most common reach types are E3 and E4 at level II in Rosgen’s classification, with cobble or gravel beds, respectively. E reaches often have wide wetland fringes, fed by overbank flooding, groundwater discharge along the valley walls, and discharge of hyporrheic flow. Hyporrheic flow is the shallow groundwater flowing immediately beneath and adjacent to the channel. It can extend many meters to the sides of the stream.
E reaches are classified into four sub-types based on channel sinuosity and form (Fig. 2):
- Sub-type ‘l’ are linear E reaches, with a sinuosity (channel length/valley length) of less than 1.3 (and often less than 1.2).
- Sub-type ‘s’ indicates E reaches with a sinuosity greater then 1.3.
- sub-type ‘a’ indicates E reaches whose channels are not visible on 1:24,000 aerial photography, but are inferable from other patterns, or obvious during a field visit.
- Sub-type ‘b’ describes bank-full linear or sinuous reaches. These reaches are backed up by an obstruction, such as a beaver dam or culvert that is improperly-sized.
 Reb stream reach; Soldotna Creek. |
 Res stream reach; middle Stariski Creek. Sinuosity = 2.52 |
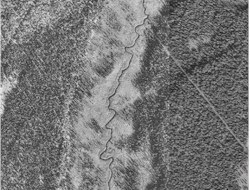 Rel stream reach; middle Ninilchick River. Sinuosity = 1.23 |

An underfit E stream reach emerging from a culvert in a wide valley near Clam Gulch.
C reaches are the probably the most familiar model of rivers, with cut banks eroding at the outside bends, point bars forming on inside bends, and wide active floodplains. Many C reaches in Cook Inlet Basin lie in underfit valleys, but still support wide active floodplains. Many portions of the floodplain do no meet wetland criteria today, but the stream will eventually meander to every part of the floodplain. Wetlands on the floodplain are abandoned oxbows, fed by hyporrheic discharge or overbank flooding, or they are fed by shallow groundwater discharge at the toeslopes of the valley walls. Uncommonly, some wetlands adjacent to C reaches are relict abandoned meander terraces, which were formed when the river drained a glacier at the end of the last glacial maximum and are now peatlands situated on terraces above the modern floodplain. The lower portion of Willow Creek has several such features.

A C stream reach, Deep Creek near its mouth, a point bar has formed on the other side of the channel.
D reaches are large braided systems fed by glacial discharge. These reaches form aggading braidplains, and are very different from the meandering C stream model of cut banks and point bars. Aggradation can be extreme, especially on the braidplain of the Ressurection and Salmon Rivers near Seward where single flood events can raise portions of the plain a meter or more above the previous base level. Braidplains are extremely active, and often are sparsely vegetated but they do support less active floodplain wetlands along their margins. A braided thread of the river channel can potentially shift its flow to any portion of the wide braidplain.

A braided D reach, the Ressurection River, in Seward. The sparse willow vegetation can potentially be replaced by a flowing channel thread at any time following a high flow event.
| Table 1. Water chemistry and plant Prevalance Index of Riverine wetlands in the Cook Inlet Lowlands. | ||||
| Map Component | pH | Alkalinity, mg/l as CaCO3 | Specific Conductance µS/cm | Plant Prevalence Index |
RB |
6.8 (18) | 54.4 (7) | 173 (11) | 2.84 (34) |
RC |
6.8 (5) | 15.0 (1) | 53 (4) | 3.05 (3) |
RD4 |
8.0 (5) | 43.9 (3) | 127 (5) | 3.07 (1) |
RDA |
6.6 (1) | 64.1 (1) | 1.93 (2) | |
Rea |
6.4 (22) | 14.2 (22) | 69 (21) | 2.32 (28) |
Reb |
6.5 (26) | 33.9 (20) | 87 (25) | 1.96 (26) |
Rel |
6.6 (20) | 21.0 (10) | 133 (16) | 2.59 (23) |
Res |
6.3 (30) | 14.5 (9) | 117 (24) | 2.43 (20) |
Explanation:
Numbers in paraentheses indicate number of samples.
pH and specific conductance are measured in the stream with a YSI 63 meter calibrated each sample. The values for Re_ streams include Res, Rel, Reb, & Rea. These values are heavily weighted toward Matanuska Valley streams where a combination of population density and the composition of underlying rocks may contribute to higher values for specific conductance there.
Plant Prevalence Index calculated based on Alaska indicator status downloaded from the USDA PLANTS database, which may use different values than the 1988 list.
NWI and HGM
Riverine wetlands are the same as the Riverine classification in the US Fish and Wildlife Service’s National Wetland Inventory (Cowardin et al 1979). Riverine 3, (upper perennial) is the most common NWI type on the lowlands, these reaches have fast velocity, gravel to boulder beds, and little floodplain development, corresponding to Rosgen’s (1996) “B” streams. R2 (lower perennial) rivers and streams are also common. These are low gradient, slow velocity “E” and “RDA” streams, although, unlike typical NWI R2 streams, floodplains may be poorly developed and oxygen deficits probably never occur. Stream-adjacent wetlands are found near braided glacial rivers which in NWI these are intermittently flooded PSS/EMJ Palustrine shrub/scrub and emergent wetlands.
The LLWW hydrogeomorphic classification of Tiner (2003) would place lowland stream-adjacent wetlands in its Lotic Stream fringe category. Type B and C streams are “middle gradient streams”; while E and RDA streams are “low gradient streams”. Rib’s are Bidirectional-nontidal River Island wetlands.
Soils and Plant Communities
| Table 2. Common soils and plant communities found in Riverine wetlands. | ||
| Map Component | COMMON SOILS | COMMON PLANT COMMUNITIES |
RB |
KILLEY | Calamagrostis canadensis streamside
Alnus viridis ssp. sinuata / Equisetum arvense Salix barclayi / Calamagrostis canadensis – Equisetum arvense |
RC |
KILLEY | Salix barclayi / Calamagrostis canadensis – Equisetum arvense |
RD4 |
TYPIC CRYAQUENTS | Alnus incana ssp. tenuifolia / Equisetum arvense |
Re |
STARICHIKOF | Salix barclayi / Calamagrostis canadensis |
RDA |
STARICHIKOF
HISTOSOLS |
Salix barclayi / Calamagrostis canadensis / Comarum palustre |
| HISTOSOLS are any organic soils greater than 40 cm deep. | ||
Cation Chemistry
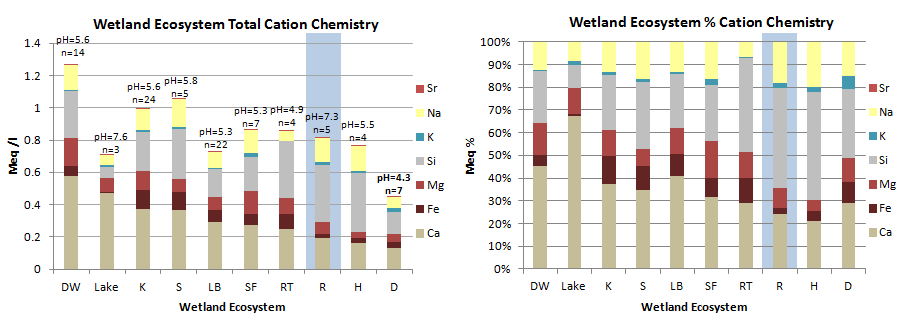
Cation chemistry by Geomorphic Component. Riverine wetlands (highlighted in blue) have generally low cation concentrations compared to other Geomorphic Components, indicating that precipitation and snowmelt strongly influence chemistry. Although calcium and silicon show the greatest concentrations, magnesium and iron concentrations in our area are high for natural waters. DW = Drainageway, K = Kettle; S = Discharge Slope; LB = Lakebed; SF = Spring Fen; RT = VLD Trough; R= Riparian; H = Headwater Fen; D = Depression.
Samples were collected from a surface pool where possible, otherwise from a separate shallow pit excavated to just below the water table. All samples were filtered through either a 0.2 micron filter using a disposable syringe, or pumped through a 0.45 micron filter using a peristaltic pump. Samples were acidified with ultra-pure nitric acid and kept cool until analysis on a direct current plasma spectrometer to about 5% accuracy (except K, 10-20% accuracy).
Riverine Wetland Types:
- AMT– Abandoned meander terraces and channels (not strictly Riverine wetlands, but associated with a few rivers and streams)
- Rel– Linear, sinuosity less than 1.3, low gradient, pool dominated, on glacial deposits.
- Res- Sinuous, sinuosity greater than 1.3, low gradient, pool dominated, on glacial deposits.
- Reb- Bank-full due to beaver dam, roads, logging debris or natural obstruction. Low gradient, on glacial deposits.
- Rea- Stream surface not discernible on aerial photography. On glacial deposits.
- Rib- Islands and bars in streams.
- RA- Steeper, step and pool morphology
- RAA- Waterfalls
- RB- Higher gradient (>2%); riffle dominated.
- RC- Floodplain developed. Point bars. Riffle/pool morphology.
- RDA- Multiple braided, low gradient, pool-dominated channels on glacial deposits.
- RD3C- Glacier-fed braided channels dominated by cobbles. Fourth of July Creek near Seward
- RD4C- Glacier-fed braided channels dominated by gravels. The Resurrection River in Seward
- RDF1- Permanently flooded ponds on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches
- RDF2- Stable water table near the surface in wetlands on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches, usually sedge dominated
- RDF3- Fluctuating water table on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches, usually shrubby
- RD4SC- Side channels on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches
- RD4T1- Low terraces on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches, often does not meet wetland jurisdictional criteria
- RD4T2- Higher terraces on the braidplains of glacier-fed reaches, often does not meet wetland jurisdictional criteria
- Rt- Tidally influenced river or stream. Usually too small to map but extends about a mile on larger streams, and several miles on the Kasilof and Kenai Rivers.
| Table 3. Summary of Cook Inlet Riverine Map Unit occurrence. | ||||
| Map Unit | N | Hectares | % Polygons | % Area |
| AMT | 165 | 1399 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| RAA | 5 | 1 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| RA | 145 | 836 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| RB | 971 | 7691 | 3.7 | 3.8 |
| RC | 28 | 6354 | 0.1 | 3.1 |
| Rea | 278 | 2159 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
| Reac | 1 | 0.4 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Reb | 148 | 1876 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Rel | 216 | 3066 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| Res | 91 | 3174 | 0.3 | 1.6 |
| Rib | 120 | 299 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| Rt | 19 | 1088 | 0.07 | 0.5 |
| RD3C | 2 | 47 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RD4C | 14 | 615 | 0.05 | 0.3 |
| RDF1 | 5 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 1.15 |
| RDF1-3 | 5 | 19 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| RDF1-4 | 1 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF12 | 3 | 15 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF1c | 5 | 5 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF2 | 5 | 17 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| RDF2-4 | 2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF21 | 4 | 18 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| RDF23 | 5 | 14 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| RDF2c | 2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF3 | 25 | 102 | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| RDF32 | 4 | 27 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| RDF34 | 7 | 25 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| RDF3c | 2 | 3 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RDF4 | 14 | 126 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| RDF43 | 3 | 41 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| RD4d | 1 | 4 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RD4SC | 32 | 170 | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| RD4T1 | 33 | 129 | .01 | 0.06 |
| RD4T12 | 1 | 15 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| RD4T2 | 106 | 699 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| RD4T21 | 5 | 153 | 0.02 | 0.07 |
| RDA | 15 | 252 | 0.06 | 0.1 |


